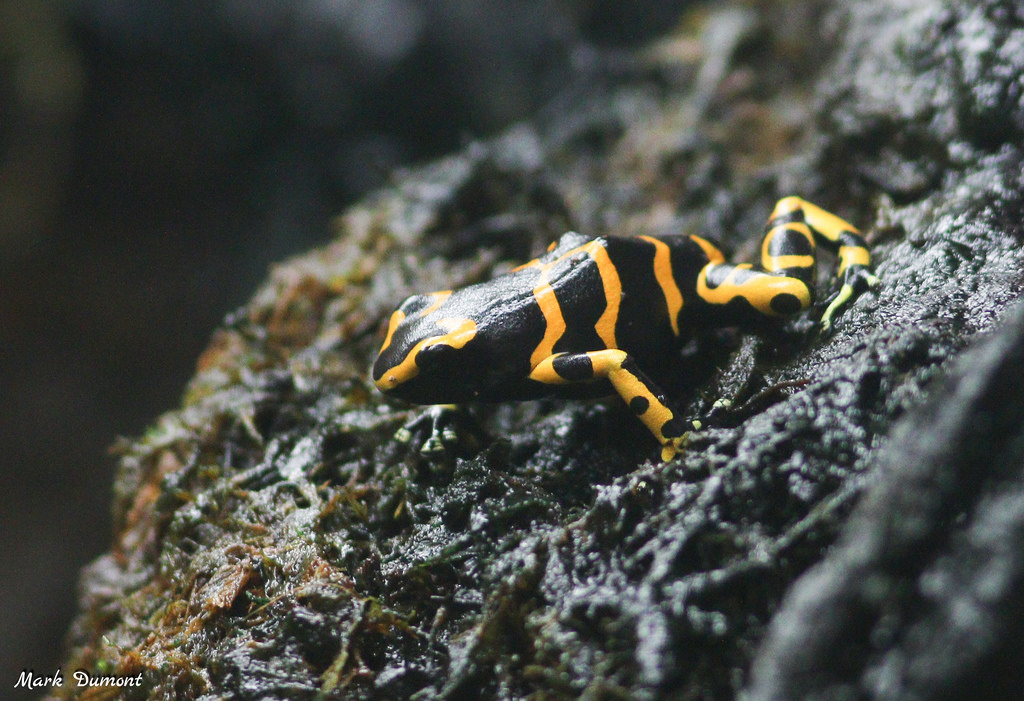
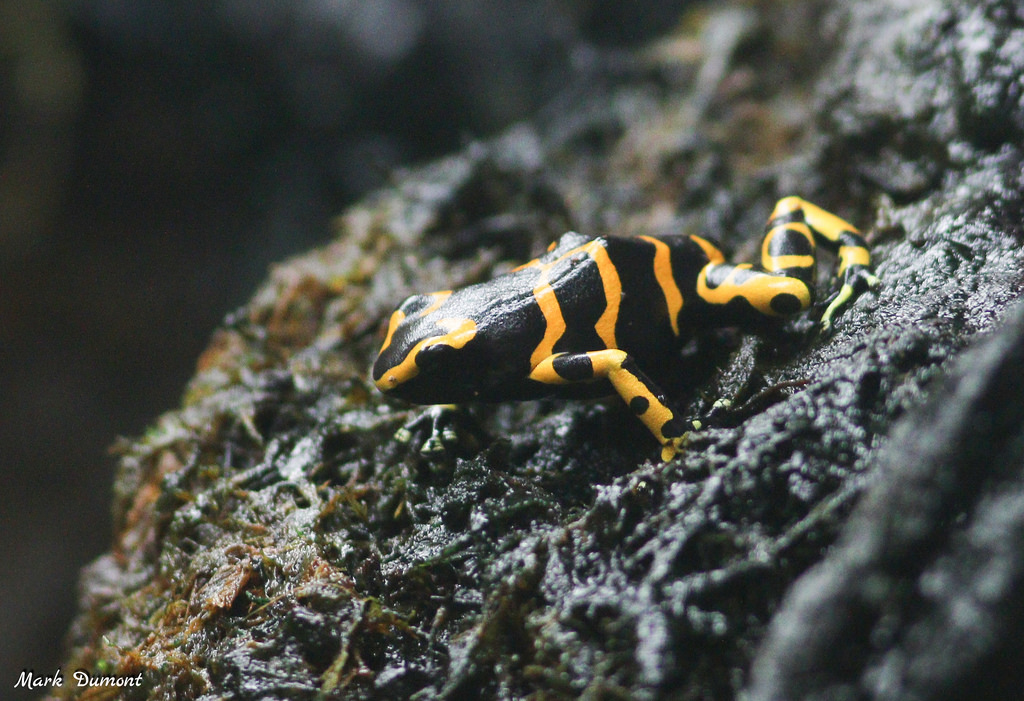
In most frogs, parental care ends with the laying of eggs, but not so for poison dart frogs. Once a female lays eggs, often on the underside of a leaf, the male guards them until they hatch into tadpoles. Then he transports each tadpole to its own tiny pool of water held within the cup-like leaves of a bromeliad plant.

Did You Know?
Researchers are studying poison dart frog toxins as a possible source of human medicine.